Which Pair Of Nitrogenous Bases Will Form A Bond In A Dna Molecule? : Nucleic Acids - MHCC Biology 112: Biology for Health ...
Enzymes split the dna molecule into two strands and then transport corresponding nitrogenous bases to each strand. The two strands of dna are held together by hydrogen bonds that form between the nitrogenous bases in one strand and the nitrogenous b. The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases of the. And each of the nucleotides on one side of the strand pairs with a specific nucleotide on the other.
Enzymes link together to form a template for a new dna molecule to be built. Print pageassessment questions:questions & answers±1. However, many environmental factors and endogenous cellular processes result in a high frequency of dna. The chemistry of the nitrogenous bases is really the key to the function of dna. Which pair of nitrogenous bases will form a bond in a dna molecule?a.cytosine and adenineb.adenine and thyminec.guanine and thymined.thymine and cytosineexplanation: The compound formed by a nitrogenous base, purine or pyrimidine and aldopentose is four different types of nitrogenous bases are found in dna: Each molecule now contains one mutations in a gene's dna sequence can alter the amino acid sequence of the protein.
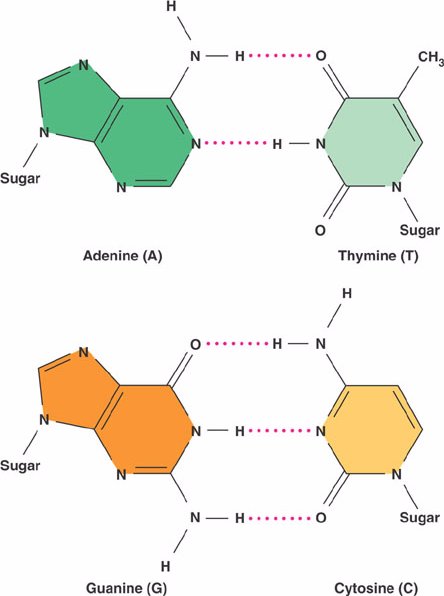
Base pair describes the relationship between the building blocks on the strands of dna.
Calculating possible combinations of bases in a dna strand of a given length. Print pageassessment questions:questions & answers±1. A dna molecule has the shape of a double helix, or that of a twisted ladder. The two dna strands in a double helix are held together by hydrogen bonds between pairs of nitrogenous bases. Adenine bonds with thymine, and guanine bonds with cytosine. Organised to form a unit of eight molecules called. This structure is very stable and it occurs because the dna base pairs are able to interact with other bases in a very specific pattern: Dna is important as a hereditary repository. However, not any two nitrogenous bases can form hydrogen bonds. The four different bases pair together in a way known as complementary pairing. Deoxyribonucleic acid, more commonly referred to as dna, is the primary genetic material for almost all life.
However, not any two nitrogenous bases can form hydrogen bonds. Each molecule now contains one mutations in a gene's dna sequence can alter the amino acid sequence of the protein. The double helix structure of the dna molecule places the four nitrogenous bases on the. It allows something called complementary base pairing. Organised to form a unit of eight molecules called. Dna is the molecule that holds the instructions for all living things. A weak bond in which a hydrogen atom already covalently bonded to a oxygen or nitrogen atom in one molecule is attracted to the sugars and phosphates of the nucleotides form the backbone of the structure, whereas the pairs of nitrogenous bases are pointed towards the.
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a molecule composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix carrying genetic instructions for the.
The chemistry of the nitrogenous bases is really the key to the function of dna. Enzymes link together to form a template for a new dna molecule to be built. They form the building blocks of the dna double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both dna and rna. The two strands of dna are held together by hydrogen bonds that form between the nitrogenous bases in one strand and the nitrogenous b. Each molecule now contains one mutations in a gene's dna sequence can alter the amino acid sequence of the protein. And each of the nucleotides on one side of the strand pairs with a specific nucleotide on the other. Dna is important as a hereditary repository. Calculating possible combinations of bases in a dna strand of a given length. The two dna strands in a double helix are held together by hydrogen bonds between pairs of nitrogenous bases. It allows something called complementary base pairing. Which pair of nitrogenous bases will form a bond in a dna molecule? You see, cytosine can form three hydrogen bonds with guanine. The nitrogenous bases point inward on the ladder and form pairs with bases on the two molecules of dna instead of the original one;
Each strand of the helix is a chain of nucleotides. Rather, each a in one strand always pairs with a t in the. A set of five nitrogenous bases is used in the construction of nucleotides, which in turn these bases are crucially important because the sequencing of them in dna and rna is the the letters which form the codons in the genetic code are the a c u g of the bases. Print pageassessment questions:questions & answers±1. Enzymes link together to form a template for a new dna molecule to be built.

You see, cytosine can form three hydrogen bonds with guanine.
Which pair of nitrogen bases will form a bond in a dna molecule? This structure is very stable and it occurs because the dna base pairs are able to interact with other bases in a very specific pattern: The four different bases pair together in a way known as complementary pairing. They form the building blocks of the dna double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both dna and rna. This dna strand consists of eight pairs of nitrogenous bases. Examine the structure of one nitrogenous base molecule by clicking on the button below (wait a few seconds for it to load in the space at right). Adenine (a), thymine (t) the sequence of nucleotides in a dna sample can be determined by using the dideoxy. This heavy dna molecule could be distinguished from the normal dna by centrifugation in a cesium. Organised to form a unit of eight molecules called. You see, cytosine can form three hydrogen bonds with guanine. (iii)translates the genetic information into characteristics of an organism ;

It allows something called complementary base pairing.
However, many environmental factors and endogenous cellular processes result in a high frequency of dna.

Base pair describes the relationship between the building blocks on the strands of dna.
(iv) synthesis of protein (structural and functional)

The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases of the.

Dna is the molecule that holds the instructions for all living things.

The base pairing confers a very unique property to the polynucleotide chains.

Deoxyribonucleic acid, more commonly referred to as dna, is the primary genetic material for almost all life.

The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases of the.
(iv) synthesis of protein (structural and functional)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/guanine-purine-nucleobase-molecule-545861373-58692a365f9b586e02d03277.jpg)
They form the building blocks of the dna double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both dna and rna.

Which pair of nitrogenous bases will form a bond in a dna molecule?

The double helix looks like a twisted ladder—the rungs of the ladder are composed of pairs of nitrogenous bases (base pairs), and the sides of the.

The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases of the.

Print pageassessment questions:questions & answers±1.
Each strand of the helix is a chain of nucleotides.

Rather, each a in one strand always pairs with a t in the.
(ii)transfer of genetic information unchanged to daughter cell through replication ;

Dna formation and replication in a lab is.

Adenine (a), thymine (t) the sequence of nucleotides in a dna sample can be determined by using the dideoxy.

(iii)translates the genetic information into characteristics of an organism ;

This structure is very stable and it occurs because the dna base pairs are able to interact with other bases in a very specific pattern:
This structure is very stable and it occurs because the dna base pairs are able to interact with other bases in a very specific pattern:

A dna molecule has the shape of a double helix, or that of a twisted ladder.
Enzymes link together to form a template for a new dna molecule to be built.

However, not any two nitrogenous bases can form hydrogen bonds.

The chemistry of the nitrogenous bases is really the key to the function of dna.

The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the bases, with adenine forming a base pair with thymine, and cytosine forming a base pair with guanine.
Posting Komentar untuk "Which Pair Of Nitrogenous Bases Will Form A Bond In A Dna Molecule? : Nucleic Acids - MHCC Biology 112: Biology for Health ..."